Neuroscience of Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness meditation, an ancient practice now validated by modern neuroscience, is a powerful tool for enhancing well-being and cognitive function. Unlike spiritual or mantra-based practices, mindfulness meditation centers on present-moment awareness, using focused techniques like mindful breathing, body scans, and attention training to cultivate self-awareness and calm. The neuroscience of mindfulness reveals that consistent practice leads to significant structural brain changes, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and anterior cingulate cortex—regions essential for executive function, emotional regulation, and memory
Research shows mindfulness meditation increases cortical thickness, enhances connectivity between brain networks, and reduces amygdala reactivity, resulting in improved emotional regulation, reduced stress, and greater resilience. Notably, mindfulness also modulates the default mode network (DMN), decreasing mind-wandering and rumination while boosting attention and concentration
Long-term mindfulness practice may even slow age-related brain degeneration, preserving gray matter and supporting cognitive health as we age. While more research is needed, the mindfulness brain benefits are clear: even ten minutes a day can foster neuroplasticity, emotional balance, and a more resilient mind.
Mindfulness is a Gateway to Present Awareness
At its essence, mindfulness is the art of anchoring oneself in the present, cultivating awareness without judgment. This gentle practice nurtures a harmonious connection between thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations, enriching our relationship with ourselves and our environment.
Structural Brain Changes: A Symphony of Growth
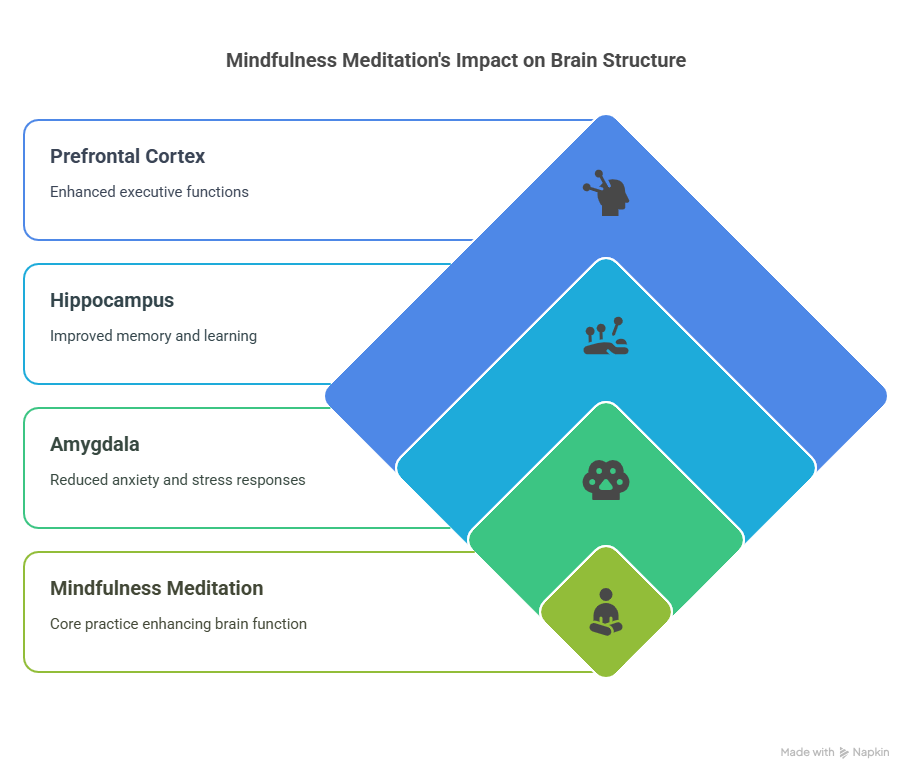
Prefrontal Cortex: Regular mindfulness meditation enhances the prefrontal cortex, the seat of executive functions. This structural brain change underpins improved decision-making, emotional regulation, and self-control.
Hippocampus: Mindfulness increases gray matter in the hippocampus, fortifying memory and learning—key pillars of cognitive vitality.
Amygdala: Through mindfulness, the amygdala—our emotional sentinel—diminishes in density, correlating with reduced anxiety and stress responses.
Functional Brain Changes: Harmonizing Connectivity
DMN stands for the Default Mode Network — a group of interconnected brain regions that become active when the mind is at rest and not focused on the outside world. It is associated with:
Daydreaming
Self-referential thoughts
Worrying about the past or future
Mind-wandering
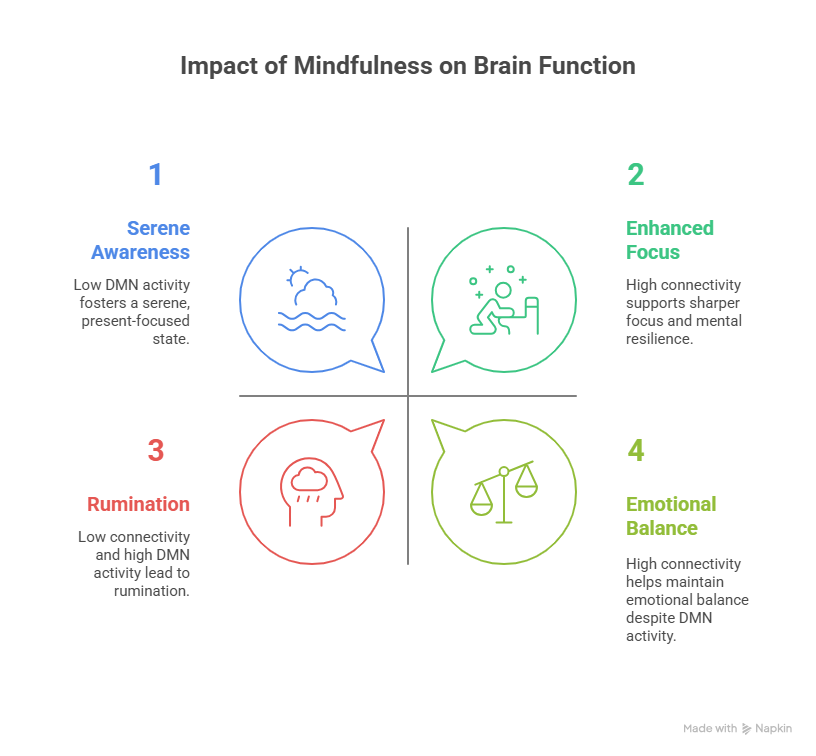
When DMN activity is high, the brain tends to ruminate or drift into unproductive or negative thought loops.
When DMN activity is low, especially during mindfulness meditation, it fosters a present-focused, calm, and aware state, reducing mental clutter and enhancing emotional regulation. This is why practices like meditation are linked to mental clarity and serenity.
Enhanced Connectivity: Mindfulness fosters robust links between brain regions, supporting emotional balance, sharper focus, and mental resilience.
Default Mode Network Modulation: By quieting the default mode network, mindfulness curbs rumination and anxiety, ushering in a serene, present-focused awareness.
Psychological Benefits: Neuroscience Meets Well-being
Emotional Regulation: Strengthened prefrontal cortex activity and a calm amygdala yield greater emotional regulation and stress mastery.
Attention and Concentration: Mindfulness amplifies attentional control, reducing distractions and enhancing productivity.
Sleep Quality: The calming influence of mindfulness soothes the nervous system, promoting restful, restorative sleep.

Integrating Mindfulness: Simple Practices, Profound Impact
Mindful Breathing: Dedicate moments to the gentle rhythm of your breath.
Body Scan Meditation: Attune to sensations throughout your body, fostering nonjudgmental awareness.
Mindful Walking and Eating: Engage fully with each step and every bite, savoring the richness of the present.
Mindfulness as a Pathway to Flourishing
The neuroscience of mindfulness reveals a tapestry of structural and functional brain changes that elevate emotional regulation, attention, and overall well-being. By weaving mindfulness into daily life, we unlock enduring benefits for mind and brain, nurturing a deeper, more serene connection with ourselves and the world.





